-

-

Archipelago Lighting
Archipelago Lighting LTG16526C18024K1 Dcor | G16.5 | Clear | 2.0W/2400K/E26/Gen-1
Add to Cart$5.96 -

-

Archipelago Lighting
Archipelago Lighting LTS14C10024K1 Dcor | S14 | Clear | 1.0W/2400K/Gen-1/E26
Add to Cart$3.96 -

-

-

EiKO
55W Duo-Tube 6500K 2G11 Base Compact Fluorescent, DT55/65/RS | EiKO
Call for PriceView Details -

Archipelago Lighting
Archipelago Lighting LTG25C20027K1 Dcor | G25 | Clear | 2.0W/2700K/Gen-1
Add to Cart$5.96 -

-

Halco Lighting Technologies
Halco Lighting Technologies T848FR12/850/BYP4/DSE/LED T848FR12/850/BYP4/DSE/LED 84888 LED T8 12.5W 48 IN
Call for PriceView Details -

Archipelago Lighting
Archipelago Lighting LTG165C35027MB Dcor | G16.5 | Clear | 3.5W/2700K/E26
Add to Cart$7.96 -

Halco Lighting Technologies
Halco Lighting Technologies BR30FL65 104070 65W BR30 Fl 130V 5M
Call for PriceView Details

Light Bulbs
Comprehensive Light Bulb Store Guide - Find the Perfect Bulb
When you’re heading out to a light bulb store, remember that different type of light bulb have their pros and cons, and your light bulb store might not have the best article for your home or commercial use. There are designated bulbs designed especially to be installed in different spaces of your venue. Our light buying guide takes a deeper look at the different bulbs to see where each should be used.
How to Pick the Right Light Bulb - A Buyer's Guide
Need help figuring out which bulb works best for each application? Do not worry anymore because Lighting and Supplies has you covered. Read this guide and educate yourself about all the nooks and crannies of light bulbs. We’re a top light bulb supplier in the US and want to provide you with the best guide to help you through the entire buying routine. Next time when you’re out looking for a substitute for the fused light bulb, you know what kind would be the best for your use case.
LED Light Bulbs - Efficiency and Versatility
LED or light-emitting diode is a lighting technology that is extremely energy-efficient and is the one you're most likely to find at the store these days. LED light bulbs provide both directional and diffused light, making them great for under-counter task lighting as well as overall room illumination.
If you’re considerate about pricing LED light bulbs are still more expensive than many other lights but they are very energy efficient, making them the most economical choice in the long run. In addition, you can now find WiFi-enabled LED bulbs that work with Google Home, Alexa, and other "smart" devices that allow you to brighten and dim lights - and even change their colors - just by speaking.
Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFLs) - Energy Saving Options
Compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) consume a quarter of the energy that incandescent bulbs do and last 10 times longer. Looking for an energy saver? CFL is your best bet! CFLs are quiet, instant-on, and have warmer color-corrected tones. They can be used anywhere you’d use a typical incandescent light bulb. However, they contain trace amounts of mercury, a harmful substance. Although the bulbs contain far less mercury than other household items, they need extra care to prevent breakage.
Fluorescent Light Bulbs for Large Spaces
The typical fluorescent light bulbs give a flat, cold light that's often bluish and harsh. It is a daylight equivalent and cannot be put on a dimmer. There are many types of fluorescents on the market, like warm ones, cool ones, and special-colored ones, and they typically produce more light and last longer than incandescent ones. They work well to light large areas like basements or attics.
Incandescent Light Bulbs - Classic and Warm Lighting
Incandescents produce a warm, inviting quality and are complimentary to skin tones. Incandescent light bulbs usually last between 700 to 1,000 hours and can be used with a dimmer; however, they're not as energy efficient as other options. Household incandescents are becoming harder to find, but they're still available as specialty bulbs for vanities, nightlights, ceiling fans, etc.
Halogen Light Bulbs - Natural Daylight at Home
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent that gives off natural daylight, known as "white light." Colors appear sharper under halogen light bulbs and they can be dimmed. They're more energy efficient than incandescent bulbs but they're more expensive and burn at a higher temperature. Most often, halogen bulbs are used in under-cabinet lighting, pendant lights, and recessed cans. Make sure you’re not bare-handed when changing the halogen bulb. The smallest residue of oil from a hand can rub off on the bulb, creating an atmosphere where the bulb in the lamp warms too quickly and can cause the bulb to explode.
Light Bulb Type Comparison Chart
Here’s a detailed light bulb comparison chart you should refer to if you want to compare the top bulb types.
|
LED |
FLUORESCENT |
HALOGEN |
INCANDESCENT |
|
|
EFFICIENCY |
Uses up to 80% less energy than an incandescent |
Uses up to 75% less energy than an incandescent |
Uses up to 30% less energy than an incandescent |
90% of energy is wasted as heat |
|
AVERAGE LIFE SPAN (HOURS) |
50,000 |
10,000 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
|
ANNUAL OPERATING COSTS |
Low |
Medium-Low |
Medium |
High |
|
LIGHT OUTPUT (WATTS/800 LUMENS) |
6-8W |
13-15W |
45W |
60W |
|
COLOR TEMPERATURE |
Varies by product; select high-quality LEDs for consistency |
Ranges from warm (3,000K) to cool (6,000K) |
Ranges from warm (2,700K) to cool (5,500K) |
Warm (2,700K) |
|
COLOR RENDERING INDEX (CRI) |
80-90+ |
Most are 60-70+ |
100 |
100 |
|
DIRECTIONALITY |
Directional |
Multidirectional |
Multidirectional |
Multidirectional |
|
DIMMABLE |
Most |
Few |
Yes |
Yes |
What to Consider When Buying LED Light Bulbs - Understanding the Different Light Bulb Store
Looking for LEDs at a light bulb store? Our experts at Lighting and Supplies want you to find the exact LED bulb you're looking for. To help in getting the best-LED light bulbs on this buying adventure, here are the main considerations worth noting before choosing the right one:
- Efficiency: Compared to conventional incandescent lamps, LED lasts longer, is more durable, and is over 5x more efficient. LED bulbs typically use only 2-10 watts of electricity
- Cost & Brightness: LED bulbs, measured in lumens and not watts, have a higher upfront cost but will have a greater lifespan in the long run
- Design: Their compact size makes them an ultra-flexible design element, allowing designers and manufacturers to create modern shapes, silhouettes, and technologies
- Cool & Mercury-freet: LEDs have no mercury and convert electricity to light without heat build-up
Understanding Light Bulb Shapes and Sizes
The most common light bulb shapes are:
- Standard Household – denoted with an A
- Candle or Decorative – denoted with a C
- Reflector – denoted with an R
- Mini Reflector – denoted with MR
- Parabolic Aluminized Reflector – denoted with PAR
- Globe – denoted with G
- Tubular – denoted with a T
All light bulb shape codes will be listed on the packaging. The shape code consists of a letter that indicates the physical shape, followed by a number that indicates the size(in 1/8th of diameter). For example, an “A19 bulb” means that these light bulbs come in a standard household shape and are 19/8 inches in size.
How Energy-Efficient Light Bulbs Compare with Traditional Incandescents
By replacing your home's five most frequently used light fixtures or bulbs with models that have earned the ENERGY STAR, you can save $75 each year.
If you replace your home's five frequently used light bulbs with models that have earned the ENERGY STAR, you can save $75 each year. Compared to traditional incandescents, energy-efficient lightbulbs such as halogen incandescents, CFLs, and LEDs use 25-80% less energy and can last 3-25 times longer.
Today's energy-efficient bulbs are available in the wide range of colors and light levels. While the initial price of energy-efficient bulbs is typically higher than traditional incandescents, newer bulbs cost less to operate, saving you money over long run and last significantly longer so you won't need to replace them as often.
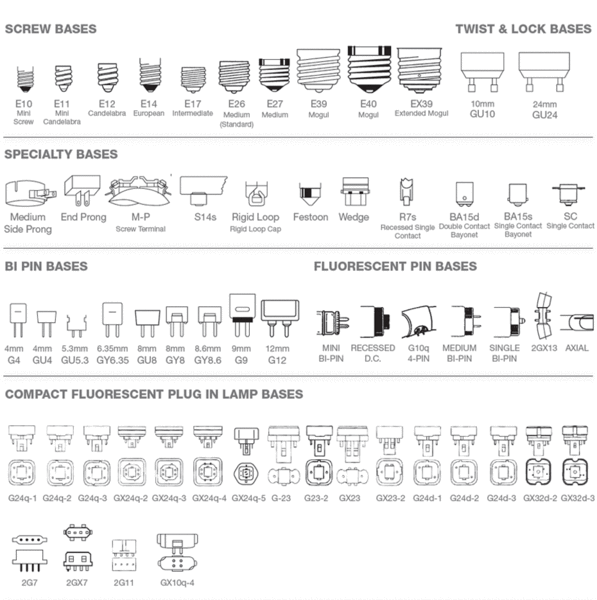
What is the difference between E26, E27 and A19? Light Bulb Base and Shape Explained
The light bulb industry serves throughout the world and there are different types of bulbs used with different bases and shapes.
Base Type
Screw in light bulb uses a base called an Edison Screw or ES base. Thomas Edison developed this base for the first light bulbs and is still in use today.
There are four commonly used thread size groups for lamps and light bulbs:
- Candelabra: E12 North America, E11 in Europe
- Intermediate: E17 North America, E14 (Small ES, SES) in Europe
- Medium or standard: E26 (MES) in North America, E27 (ES) in Europe
- Mogul: E39 North America, E40 (Goliath ES) in Europe.
The number following the E indicates the size in mm of the external thread screw. Thus E26 has a 26 mm base diameter. You may see low-cost LED bulbs using an E27 base on eBay and Amazon. While these technically work in E26 bases, they are not strictly designed for the US market, and the bulb may lack a proper North American, UL, or ETL safety certification and therefore should be avoided.
At lightingandsupplies.com, rest assured you will only be buying the highest quality light bulbs and light fixtures from the most reputable lighting brands in the US.
Bulb Shape
After learning about E26 and E27 bases you need to know what A19 or bulbs with an A designation mean. A type describes a bulb that has a pear-like shape. The number that follows the "A" within the A series indicates the bulb width in 1/8th inch units or millimeters. The most commonly used A-series bulb type is the A19 bulb which is 2 3⁄8 inches (60 mm) wide at its widest point and approximately 4 3⁄8 inches (110 mm) long. This is the classic shape that most people are used to when shopping for light bulbs.

Image Source: Earthled
What's The Difference Between An A19 Bulb & E26 Bulb?
To add clarity to this comparison, when you’re looking at bulbs for your home use at the light bulb store here in the States, they are A19 bulb with an E26 base. Lighting terminology can be confusing if you're not in the industry. If you've seen what looks like the same type of light called both an A19 bulb and an E26 bulb, you might be wondering what the difference is.
A19 refers to the shape and size of the bulb itself. "A" stands for Arbitrary - just the name of the shape that's familiar to most of us. "19" refers to the size - in this case, 19/8" (or 2 3/8") across. E26 refers to the type and size of the base - the part that goes into the light socket. "E" refers to "Edison," which is the type of "screw in" style base people in the US are most familiar with and 26 refers to 26 mm across.
Exploring the Different Types of Light Bulbs
In the last two centuries, light bulbs have seen tremendous development and significant improvement regarding efficiency, quality of light, density, and energy conservation. Even though, we still carry the basic image of a light bulb in our mind; light bulbs are available in different shapes, sizes, voltages, and materials. Lightingandsupplies.com offers lamps and light bulbs manufactured by LED lighting brands like EiKO, RAB Lighting, MaxLite, naturaLED, Westgate Lighting and more.
Here is the list of the five most common types of Light Bulbs along with their respective advantages.
1. Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs are the typical tungsten filament bulbs that glow when the current passes through them, surrounded by a vacuum or nitrogen gas. The bulbs are available in different sizes including GLS, globe, candies, and mushrooms. However, the sudden current flow causes the filament to heat and burn out, causing energy waste with only 700–1000 hours lifespan. They’re the most common bulb types since the invention of bulbs and are only recently replaced by newer lighting technology like LEDs, Fluorescent, and HID bulbs.
2. Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent bulbs are more complex than the incandescent. In a fluorescent tube, the electric current passes between the cathodes, exciting mercury and other filled gasses inside, radiating energy. The phosphorous coating at the outside converts radiant energy into visible light. The fluorescent lamps use less energy to produce the same light amount and can last longer. However, these are difficult to dispose of due to mercury filling.
3. Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL)
The CFL are designed to replace incandescent bulbs in homes and commercial buildings. Working on the principle of fluorescent lamps, they produce the same amount of light with less power. It consists of multiple tubular loops, filled with mercury, and resembles an incandescent bulb. They have a longer lifespan of up to 10,000 hours, are more energy efficient, and have higher luminous efficiency. But, the mercury in the loops makes them difficult to dispose of.
4. Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps are an improved version of incandescent bulbs in which tungsten filament is wrapped in a compact transparent envelope. The bulb takes its name from filling a small amount of Halogen with an inert gas. The inert gas increases the brightness and lifespan of the bulb, resulting in higher luminous efficiency. These lamps are also smaller in size compared to the incandescent bulbs.
5. Light Emitting Diode (LED)
LED bulbs are becoming increasingly common because of their energy efficiency and varying light colors. LED is a semiconductor device in which electricity is applied to the negatively charged diode, resulting in the flow of electrons and release of the photon. An LED bulb consists of multiple diodes producing the required amount of light. As a semiconductor, the LEDs are highly energy efficient and can produce brighter light.
Top-Rated Light Bulb Supplier & Authorized Dealer
Lightingandsupplies.com is a lighting distributor of Indoor & Outdoor Commercial and Residential light fixtures and light bulbs. Based in the US, we carry the top light bulb supplier tag from top LED lighting brands like EiKO, RAB Lighting, MaxLite, naturaLED, Westgate Lighting, and more of the Top Lighting Manufacturers in the United States. We also carry a wide variety of Horticulture products by Hydrofarm, along with ceiling fans by RP Lighting+Fans. Lightingandsupplies.com also provides rebate programs, expert lighting design advice, and lighting audits for large projects. As a wholesaler, authorized dealer, and bulk distributor of lighting products, we take pride in our customer-focused 100% satisfaction guarantee and return policy.
For more information, call 888-325-4448 or email: info@lightingandsupplies.com.





























